Auditory Processing Difficulties
Listening DifficultiesHow Our Brain Processes What We Hear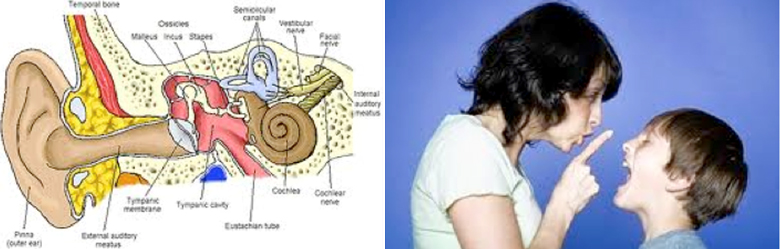
Listening DifficultiesHow Our Brain Processes What We Hear

What Is Auditory Processing Difficulty
www.thetenminutetutor.com

- Auditory Processing Disorder (APD) (CAPD) represents an inability to attend, discriminate, recognise, understand or analyse auditory information.
- This can adversely impact on a person’s ability to listen, comprehend and learn – Specifically in the area of learning to read or thinking to write and then spell accurately.
- There may be history of ear infections or fluid in the ears.
Symptoms of APD
- Difficutly concentrating
- Easily Distracted
- Can’t remember multi-step directions
- Misses instructions or mixed them up
- Is often in the wrong place at the wrong time
- Can appear to have a poor memory
- Needs more time or repetition of instructions
- Has low academic performance
- Has difficulty with correct pronunciation of words
- Has difficulty with reading comprehension, spelling and vocabulary
- Cannot hear sounds in words to spell and write them
Why Would You Have Auditory Processing Testing Done?
The individual who is having difficulty

- Litening to instructions – in and out of the classroom and staying focused in class.
- With both receptive (hearing) and expressive language (speaking).
- Decoding language – speaking, writing, spelling, understanding rhyme, beat and rhythm.
- With background noise
 Auditory Processing
Auditory Processing
- Get a hearing test
- With both receptive (hearing) and expressive language (speaking).
- Auditory processing testing by an Audiologist
- May take between 1.5 – 3 hours and involve a sound booth and a set of headphones.
- Often these tests isolate each ear and present a range of hearing, listening, speaking, reading, spelling and memory challenges.
Tests Can Assess

- Auditory Figure ground Discrepancy
- Filtered Words
- Competing words, sentences and numbers
- Sentences that are distorted and also delivered at various speeds
- Memory using numbers forward numbers reversed, words and sentences
- Attention – auditory and visual
How To Help Children With It

- Reduce background noise
- Seat children towards the front of the class
- Ask for quiet when giving instructions
- Arrange a cue or make contact with a child before giving instructions
- Get children to repeat instructions back
- Provide additional support material – audio and visual
- Allow a child to use earplugs, headphones or an Ipod on silent or with select music
- Avoid rooms that echo or reverberate – open plan
- Listening devices are available to assist further
- Audio devices are also available
- Have face to face, line of sight when giving instructions – Provide a visual cue, a verbal cue or a sound like a bell, a whistle, clap…
- Change your voice – high, low, soft, loud, funny accent
- Keep instructions short 1.2.3 method, key word method; lunchbox, readers, planners
- Start reducing repeats, train them to listen over time and reward them accordingly
Commercial Programs
- TTRS – Touch Type Read Spell
- Auditory Stimulation Programs – Listening training
- CD Home Program – Can support centre based programs
- Cellfield – Uses acoustically modified sound to assist auditory perception includes visual experiences, eye tracking and working memory
- Fast ForWord – Builds oral language comprehension, phonemic skills, expands vocabulary, sentence comprehension, syntax, working memory and logical reasoning